Motorcycle Refueling/Filling Equipment—Motorcycle Refilling Machine
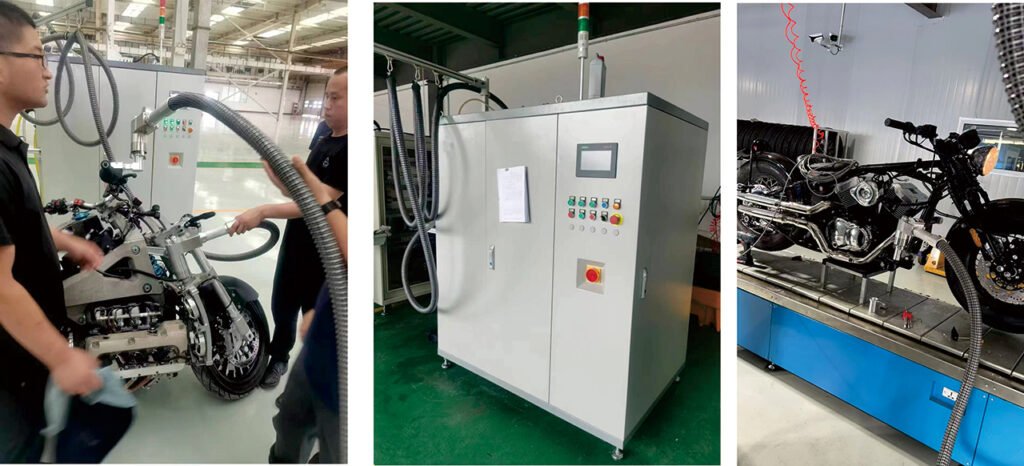

Below are the main types of filling machines commonly used:
1. Vacuum Quantitative Filling Machine
This is the most core and commonly used filling equipment, designed for fluids requiring extremely high precision in volume or weight.
- Primary Applications:
- Engine Oil Filling: Precisely fills the factory engine oil.
- Transmission/Gear Oil Filling: For gear oil in the engine or separate transmission.
- Final Drive Gear Oil Filling (if applicable): For three-wheeled or specific models.
- Coolant Filling: Filling and bleeding the cooling system of liquid-cooled engines.
- Brake Fluid Filling & Bleeding: Fills at the master or slave cylinder, potentially integrating automatic bleeding functions.
- Fork/Shock Absorber Oil Filling: Precisely injects hydraulic oil into front forks and rear shocks.
- Working Principle:
- Evacuation: The machine first connects its filling nozzle to the vehicle’s filling port and evacuates (draws a vacuum on) the system (e.g., engine oil galleries, cooling system) or container.
- Quantitative Filling: Under vacuum or pressure equilibrium, the machine precisely pumps the fluid into the system based on a preset volume or mass.
- Error-Proofing & Traceability: Filling data (e.g., actual fill quantity, fill time, station ID) is automatically uploaded to the factory’s MES (Manufacturing Execution System) for quality traceability.
- Advantages:
- Extremely high precision (can reach ±1 gram or milliliter).
- High speed, suitable for high-cycle production lines.
- Prevents air bubbles (critical for coolant, brake fluid).
- Fully automated process with data logging.
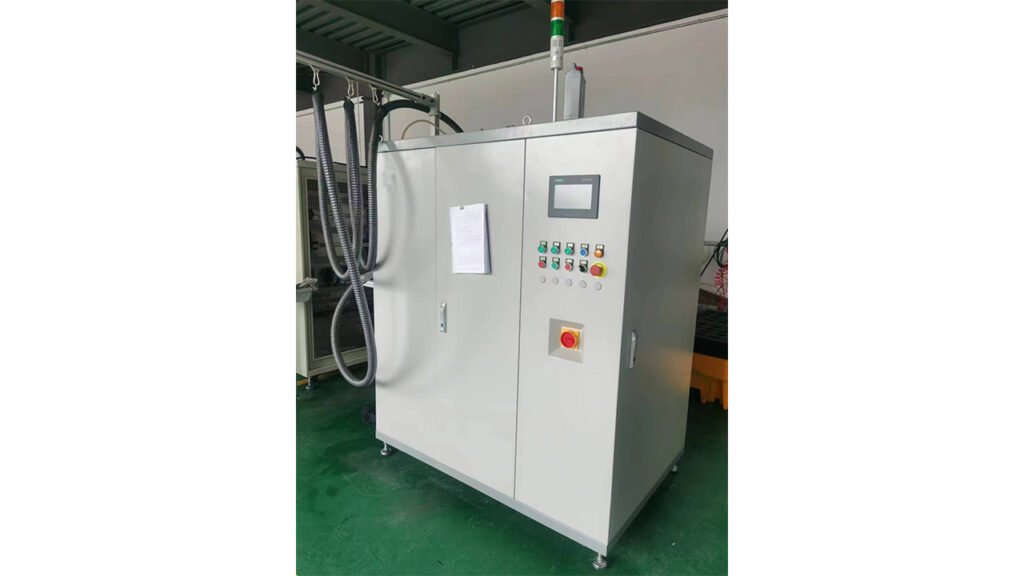

2. Quantitative Filling Machine (Non-Vacuum)
Used for stations requiring high precision but where vacuum evacuation is unnecessary or impractical.
- Primary Applications:
- Fuel Filling: Adding a small amount of starting fuel to the tank (requires explosion-proof design due to high safety standards).
- Washer Fluid Filling: Filling the windshield washer reservoir.
- Lubricant filling for some auxiliary systems.
- Characteristics: Uses high-precision flow meters or servo pumps to control fill quantity. Structurally simpler than vacuum fillers.
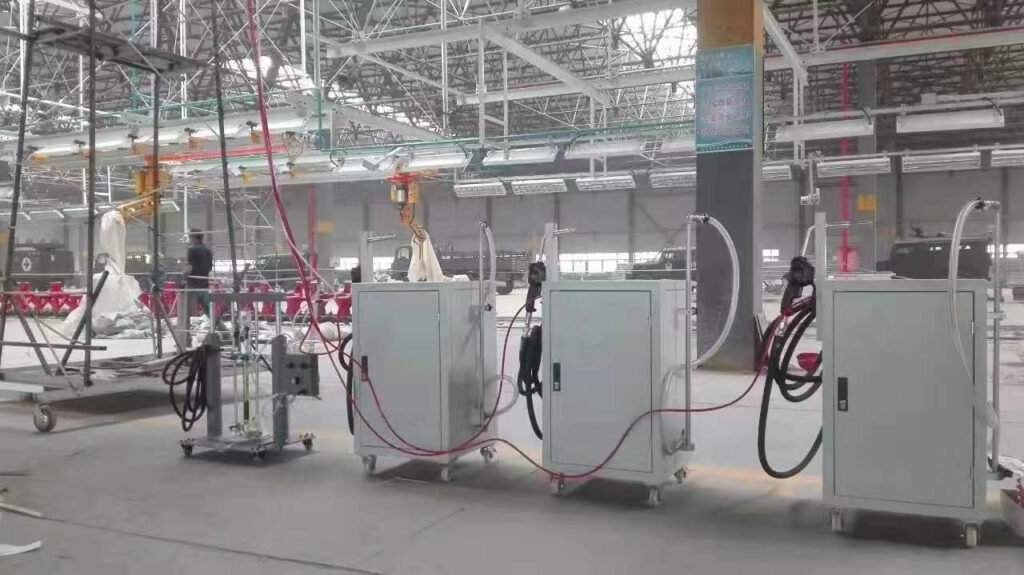

Core Requirements for Filling Equipment
- High Precision & Repeatability: Ensures consistent fill quantity for every vehicle, forming the foundation of quality control.
- High Cycle Rate & Reliability: Must match the production line’s speed with extremely low failure rates.
- Flexibility & Intelligence: Must adapt to “mixed-model” production with quick changeover capabilities.
- Safety: Especially for fuel filling, must comply with strict explosion-proof standards.
- Cleanliness & Environmental Protection: Equipment must have good sealing (no leaks), with designs for waste fluid recovery and handling.