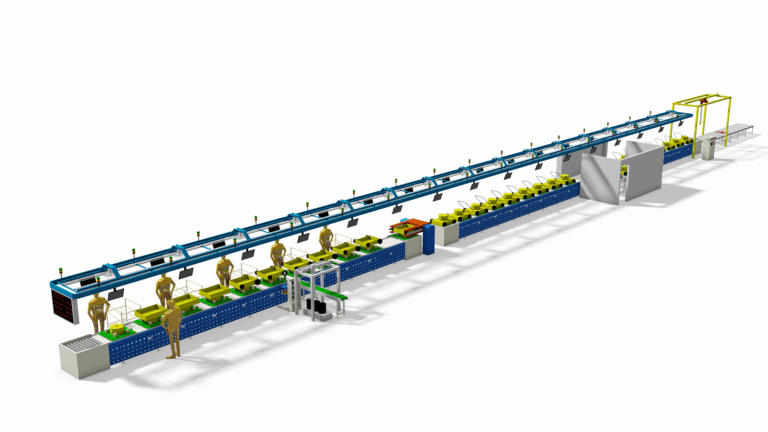
How to set up an E-scooter Assembly Line factory?—How to set up an Electric Motorcycle Assembly Line factory?
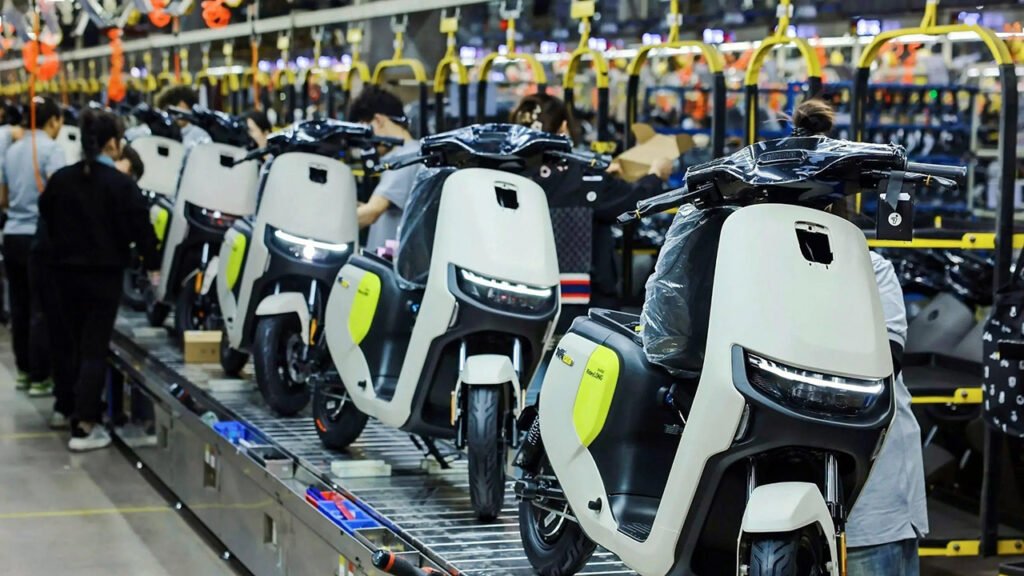

E-scooter Assembly Lines are suitable to Assemble/Produce E-scooters, 2 wheel Scooters, 2 wheel Electric-cycles, 2 wheel E-Bikes, 2 wheel Motorcycles, Bicycles, Bikes, and so on. (Sometimes, suitable for the production of Tricycles.)

How to Establish a Two-Wheel Electric Vehicle (E-bike/E-scooter) Factory
Phase 1: Strategic Planning & Preparation
This is the most critical step, determining the success or failure of the factory.
- Market Positioning & Product Definition:
- Product Type: Will it be electric mopeds, or electric motorcycles? Different categories have completely different technical standards, qualification requirements, and sales channels.
- Target Market: Domestic market or export?
- Competitive Advantage: Will it be cost leadership (value for money), technology leadership (long range), design leadership, or differentiation (specific features)?
- Product Planning: Define the first 1-3 models to launch, specifying their specifications, parameters, target price points, and selling points.
- Business Plan & Fundraising:
- Detailed Business Plan: Should include market analysis, product planning, investment budget, production cost analysis, sales forecasts, profit projections, risk assessment, etc. Used for financing and internal guidance.
- Capital Requirement Assessment:
- Fixed Assets: Land/factory building, production line equipment, testing equipment.
- Working Capital: Raw material procurement, R&D expenses, personnel salaries, marketing expenses, certification costs.
- Scale Determines Investment: Consider phased investment, starting with an assembly line and gradually adding capabilities like frame manufacturing and painting.
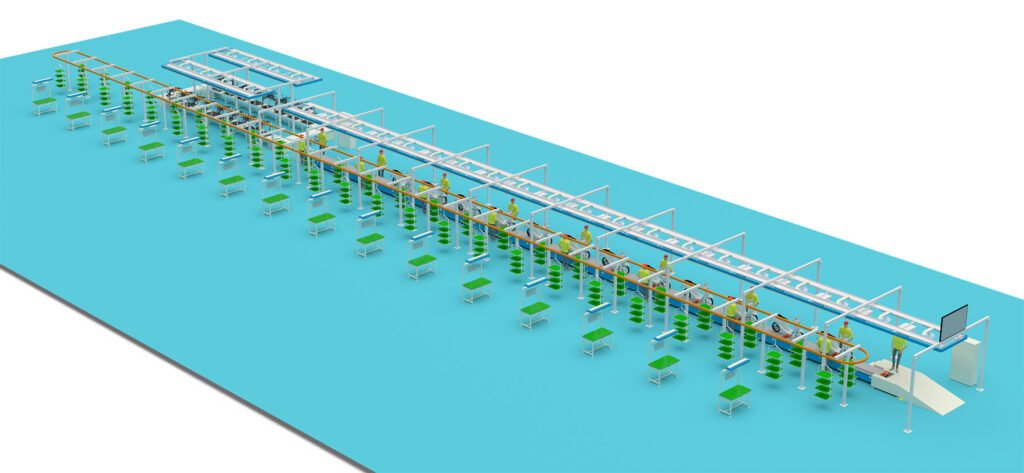
Phase 2: Factory Construction & Supply Chain Setup
- Site Selection & Facility:
- Location Choice: Consider industrial equip, logistics convenience, labor costs, and policy incentives.
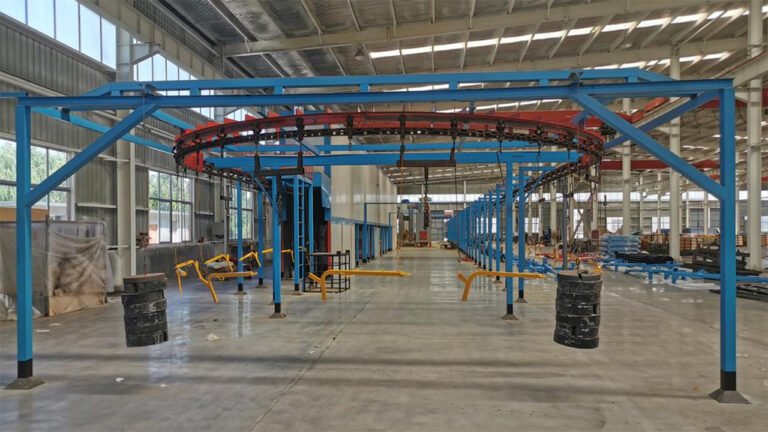
- Facility Requirements(optional): Based on process planning, typically need stamping/welding workshop, painting workshop, assembly workshop, warehouse area, R&D/QC center, office building. The painting workshop has the highest environmental requirements; outsourcing frame painting can be considered to reduce initial investment.
- Core Team Building:
- Key Personnel: Recruit or partner with experienced core team members, including:
- General Manager/Factory Director: Overall management.
- Technical/R&D Director: Responsible for product design, Bill of Materials (BOM), technical standards.
- Production Director: Responsible for production line planning, processes, efficiency.
- Supply Chain Director: Responsible for procurement and supplier management.
- Quality Director: Responsible for the quality control system.
- Key Personnel: Recruit or partner with experienced core team members, including:
- Supply Chain System Development:
- Core Component Supplier Development:
- Key Purchased Parts: Battery (cells, PACK), motor, controller, charger, frame (can be made in-house or purchased), tires, brakes, lights, instrument cluster, plastic parts (covers).
- Strategy: Establish a strict supplier quality engineering (SQE) system, build stable relationships with top-tier suppliers (e.g., Xingheng, Tianneng, Bosch, CATL) or cost-effective second-tier suppliers.
- Make-or-Buy Decision: Decide which parts to manufacture in-house (e.g., frame welding, wire harness processing, assembly) and which to purchase, based on investment and capability. Initially, it is recommended to start with SKD/CKD assembly, gradually increasing vertical integration.
- Core Component Supplier Development:
- Production Line Planning & Equipment Procurement:
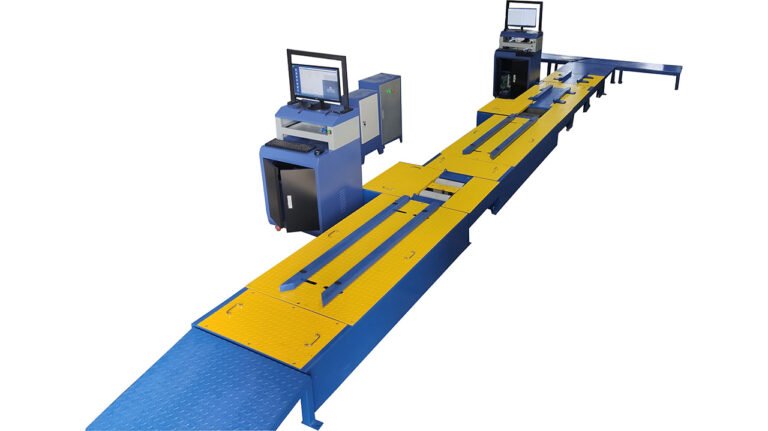
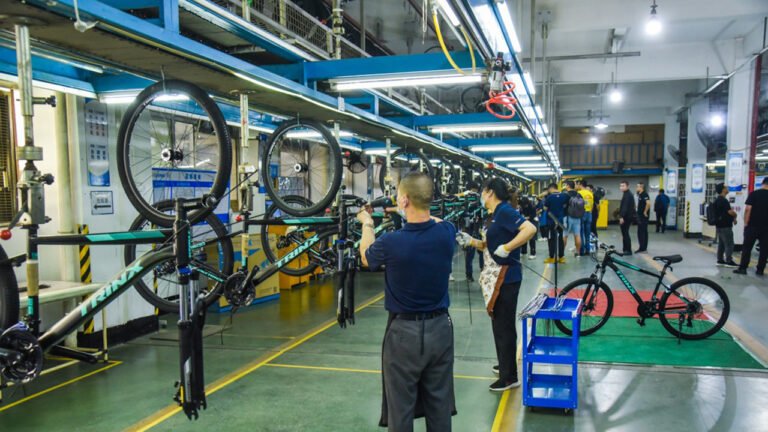
- Final Assembly Line: Conveyor or pallet line, with multiple stations (frame loading, fork installation, wheel assembly, motor installation, wiring, battery installation, debugging, quality inspection, etc.).
- Welding Line: Robotic welding workstations (high investment, stable quality) or manual welding stations.
- Painting Line: Pre-treatment (derusting, phosphating), painting, baking. Environmental protection equipment (waste gas/water treatment) is a key and challenging point.
- Testing Equipment: Whole vehicle performance test line (speed, braking, range), circuit tester, battery testing equipment, salt spray test chamber, etc.
- Logistics Equipment: Racking, forklifts, AGVs, etc.
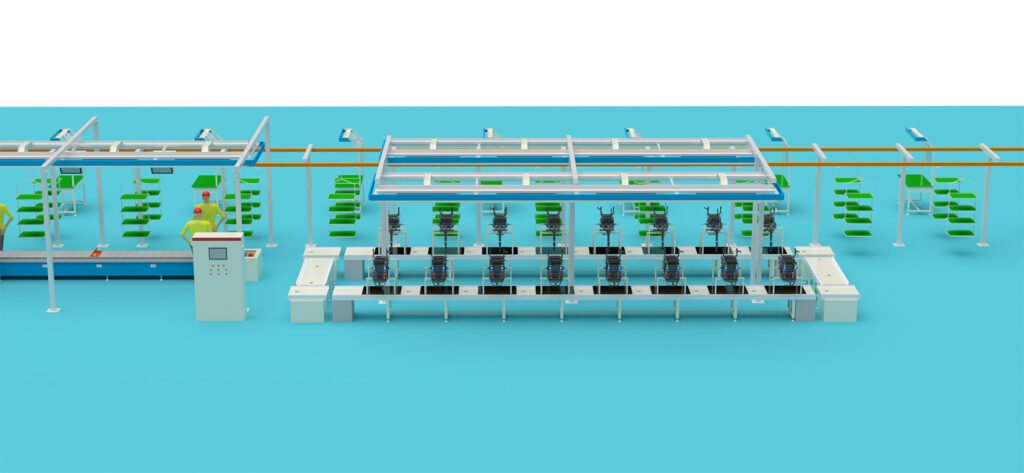
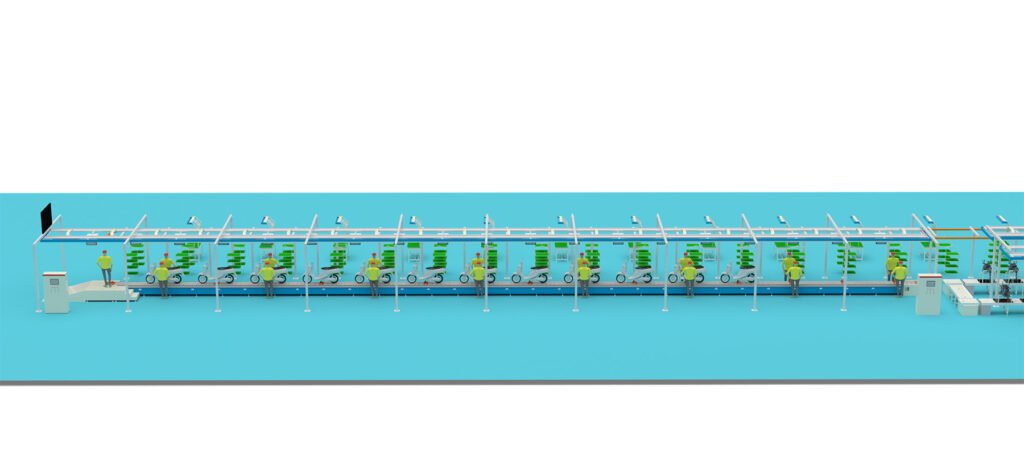
Phase 3: Product R&D & Production Introduction
- Product R&D & Prototyping:
- Industrial Design (ID) & Mechanical Design (MD): Complete appearance, frame structure, and plastic part design.
- Electrical Design: Design electrical schematics, wiring diagrams, and match the “Three Electric” system (battery, motor, controller).
- Prototype Building & Testing: Build functional prototypes, conduct rigorous performance, safety, and durability testing, and modify designs.
- Tooling/Mold Making: Create molds for parts requiring them, such as plastic parts and frames. This is a significant investment.
- Production Process & Quality System Establishment:
- Develop Process Documentation: Assembly work instructions, welding process sheets, inspection standards, etc.
- Establish Quality Management System: establish full-process quality control points.
- Pilot Production (Low Volume): Validate the stability of the production line, processes, and supply chain, producing vehicles for certification and market testing.
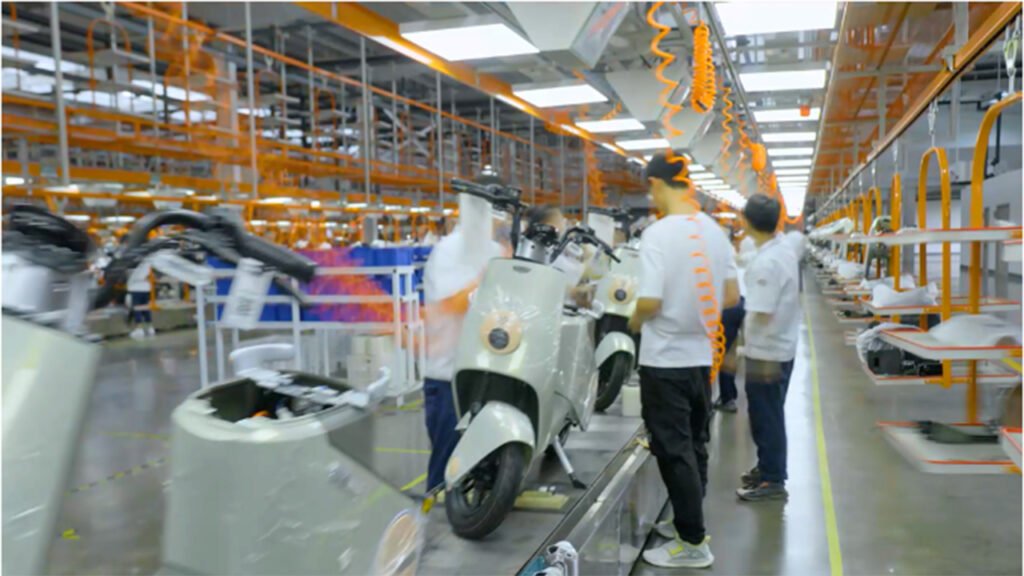

Phase 4: Mass Production, Sales & Continuous Improvement
- Mass Production Ramp-up: Gradually increase output, resolving various issues exposed during the initial production phase.
- Brand & Channel Development:
- Brand Positioning & Marketing: Establish brand image through online and offline promotion.
- Sales Channels: Establish a distributor network, open direct stores, cooperate with e-commerce platforms, and develop corporate clients (shared mobility, delivery rental companies, etc.).
- After-Sales Service System Development: Establish a national or regional after-sales service system to provide maintenance, parts, and technical support. This is crucial for brand reputation.
- Continuous Optimization: Collect market feedback, iterate products, optimize costs, and improve production efficiency and quality.
Entry-Level Suggestions
If you are new to manufacturing, consider starting with a lighter model:
- Start with Assembly: Lease a standard facility, purchase all components (frame, plastic parts, three electric systems, etc.), and focus on assembly, debugging, branding, and sales. Gradually accumulate experience and capital before moving upstream.