How to Establish a Bike Assembly Line Factory?
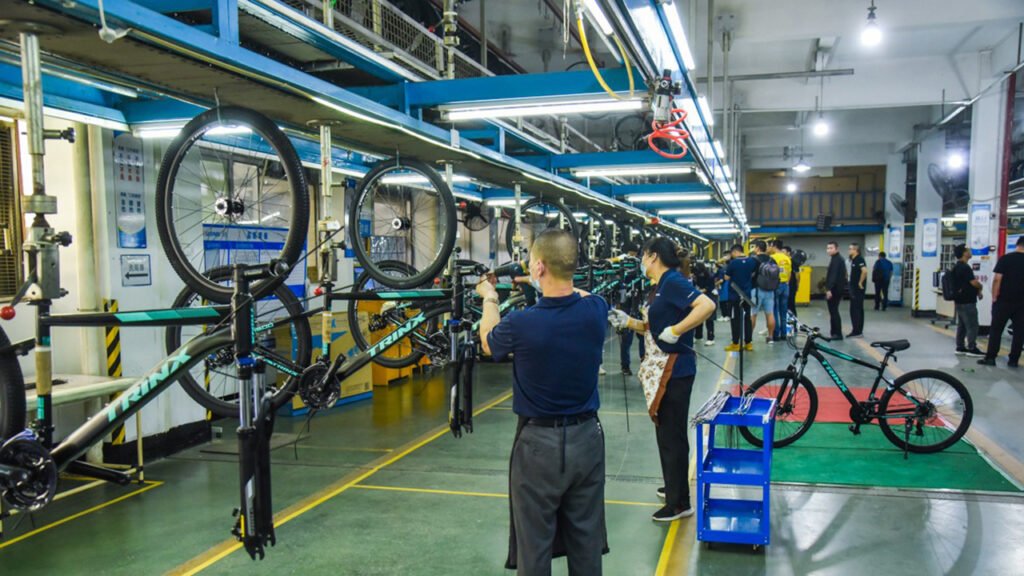

Bike Assembly Lines are suitable to Assemble/Produce Bicycles, Bikes, 2 wheel Motorcycles, 2 wheel Scooters, 2 wheel Electric-cycles, 2 wheel E-Bikes, and so on. (Sometimes, suitable for the production of Tricycles.)

Phase 1: Research & Planning
- Market Analysis: Research demand, target market (commuter, mountain, kids, e-bikes)
- Business Plan: Define product line, production capacity (bikes/day), budget, ROI projections
- Location Selection: Consider logistics, labor availability, utility costs, tax incentives
- Legal Requirements: Business registration, environmental permits, safety certifications
Phase 2: Factory Design & Layout
- Assembly Line Design:
- Straight-line or U-shaped layout
- Calculate cycle time per station
- Balance workloads across stations
- Space Requirements: Minimum 10,000-20,000 sq ft for medium-scale operation
- Key Areas: Receiving, frame prep, assembly line, quality control, testing, packaging, shipping
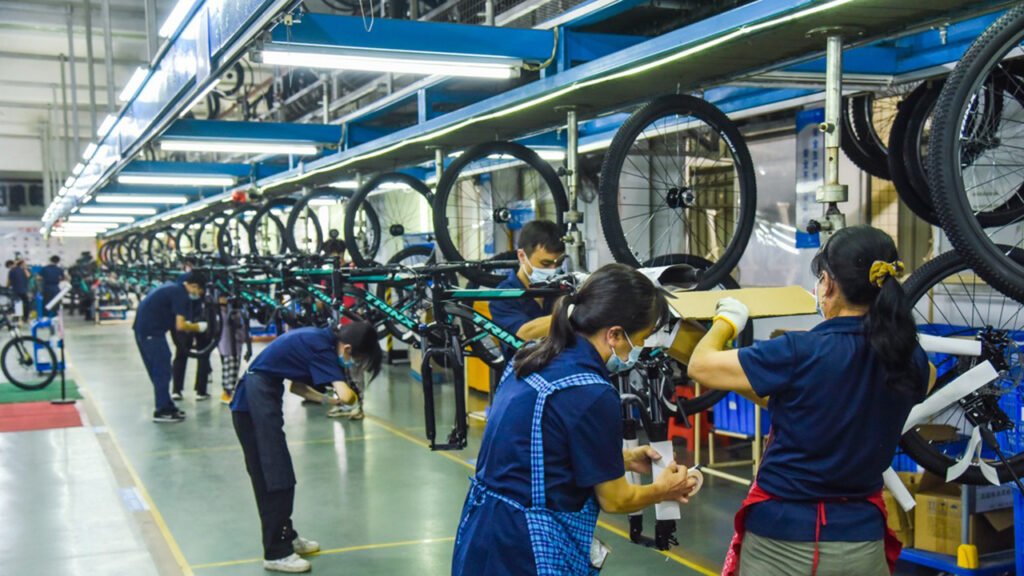

Phase 3: Equipment & Supply Chain
- Essential Equipment:
- Frame jigs and fixtures
- Wheel truing stands
- Drilling/tapping machines
- Torque wrenches and specialized tools
- Conveyor system (manual or powered)
- Testing equipment (brake testers, alignment tools)
- Supply Chain Setup:
- Source frames, components (groupsets, wheels, tires)
- Establish relationships with multiple suppliers
- Implement inventory management system
Phase 4: Production Process Design
- Typical Assembly Stations:
- Frame preparation (facing, chasing, cleaning)
- Fork and headset installation
- Bottom bracket and crankset installation
- Wheel assembly (spoking, truing, tire mounting)
- Drivetrain installation (derailleurs, chain, cassette)
- Brake system installation
- Cockpit assembly (handlebars, stem, shifters)
- Final assembly (saddle, pedals, accessories)
- Quality control and testing
- Cleaning and packaging
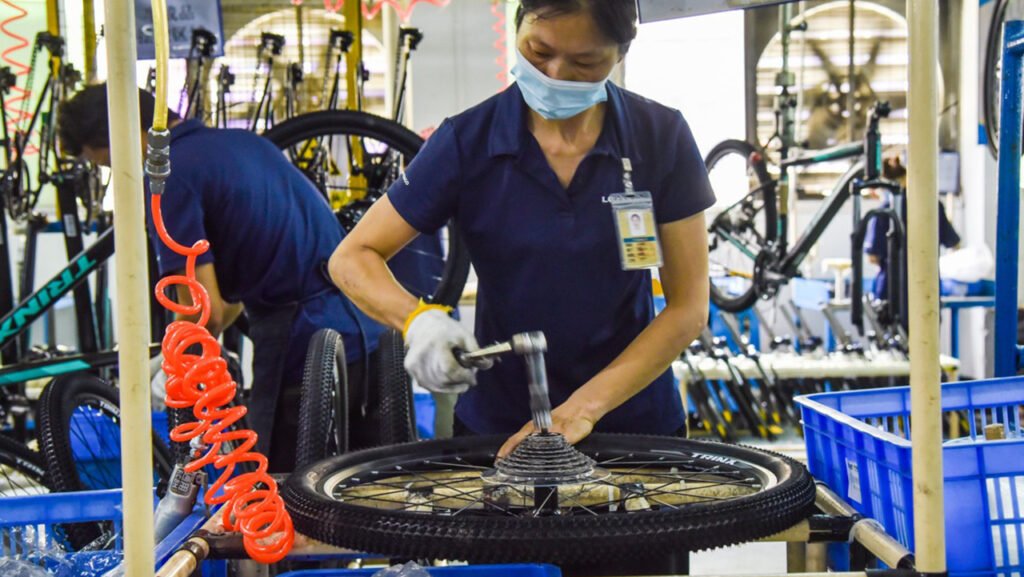

Phase 5: Human Resources
- Staffing Needs:
- Line workers (6-15 per shift depending on volume)
- Quality control inspectors
- Maintenance technicians
- Supervisors and managers
- Training Program: Develop standardized work procedures, quality standards, safety protocols
Phase 6: Quality Control System
- Inspection Points: Incoming parts, in-process checks, final inspection
- Testing Procedures:
- Brake performance tests
- Gear shifting accuracy
- Wheel trueness and spoke tension
- Frame alignment checks
- Safety torque verification on all critical bolts
- Compliance: Meet ISO 4210 or local safety standards
Phase 7: Implementation Timeline
- Typical 6-9 Month Timeline:
- Months 1-2: Planning and financing
- Months 3-4: Facility setup and equipment installation
- Months 5-6: Hiring and training
- Months 7-8: Trial runs and process refinement
- Month 9: Full production start
Key Success Factors
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Minimize waste, optimize flow
- Supplier Relationships: Ensure quality components and reliable delivery
- Skilled Labor: Invest in proper training
- Quality Focus: Build reputation for reliable products
- Flexibility: Ability to handle different bike models and customizations
Common Challenges to Anticipate
- Supply chain disruptions for specialized components
- Maintaining consistent quality with manual assembly processes
- Seasonal demand fluctuations
- Thin profit margins requiring efficiency optimization
Start with a pilot production run to identify bottlenecks before scaling up, and consider specializing in a particular bike niche to differentiate your factory in the competitive bicycle market.