Components Coating Conveyor—Spray Painting Conveyor Line—different kinds of Painting conveyors
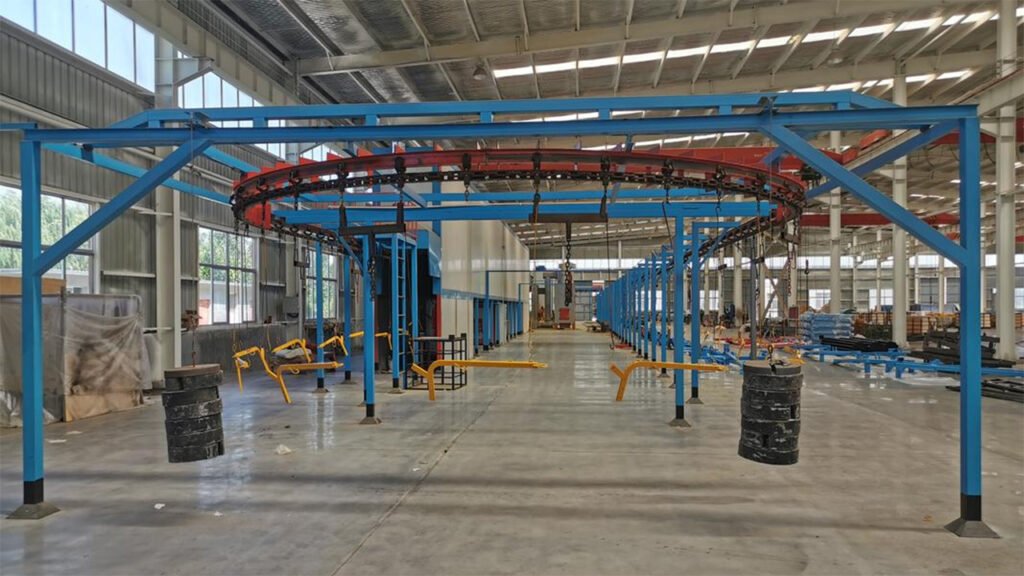

1. Core Components
A typical spray painting conveyor line system usually includes:
- Conveying Equipment (Core Carrier):
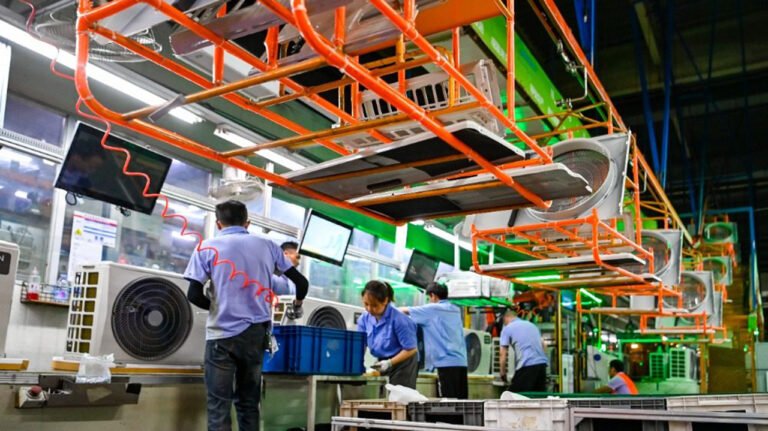
- Types: Overhead chain, floor-mounted chain (skid/trolley system), belt conveyor, roller conveyor, etc. The overhead chain is the most common type, suitable for small and medium-sized parts (e.g., home appliances, hardware).
- Function: Provides power to pull the “carriers” (hangers, skids) holding the workpieces.
- Workpiece Carrier / Hanger:
- Hooks, racks, turntables, skids, etc. These are specially designed based on the workpiece shape to fix and present the workpiece.
- Drive and Tensioning System:
- Drive Station: Provides power for the movement of the chain or track.
- Tensioning Device: Maintains proper tension in the conveyor chain to prevent slipping or sagging.
- Track System:
- Guides the path of the conveyor chain and carriers, including straight sections, horizontal/vertical curves, lift sections, etc.
- Control System:
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): The brain of the system, controlling start/stop, speed, and coordination with spraying equipment.
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface): Touchscreen for operators to monitor and set parameters.
- Identification System: Such as RFID or barcode readers, to identify different workpieces and call up corresponding spraying programs.
- Safety and Auxiliary Facilities:
- Emergency stop switches, safety light curtains, guardrails, lubrication systems, exhaust ducts, etc.
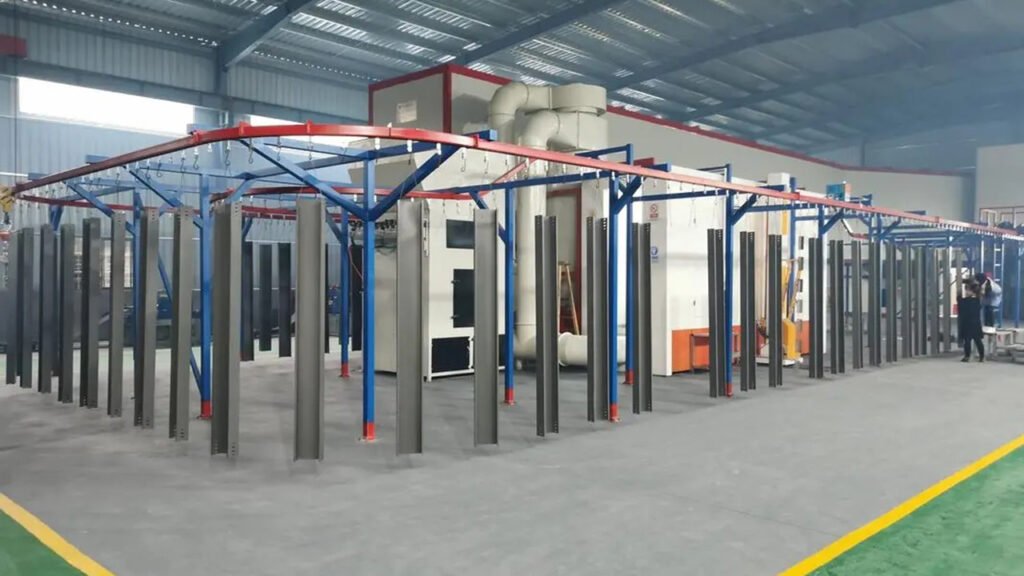

2. Main Workflow (Taking Automatic Spraying as an Example)
- Loading / Hanging: Workers fix workpieces onto hangers at the starting end of the line. This can be manual or automated by robots.
- Pre-treatment: The conveyor line carries workpieces sequentially through pre-treatment stages (e.g., degreasing, rinsing, phosphating, drying).
- Spraying Zone:
- Preparation: Before entering the spray booth, workpieces may pass through an automatic blow-off station (for dust removal).
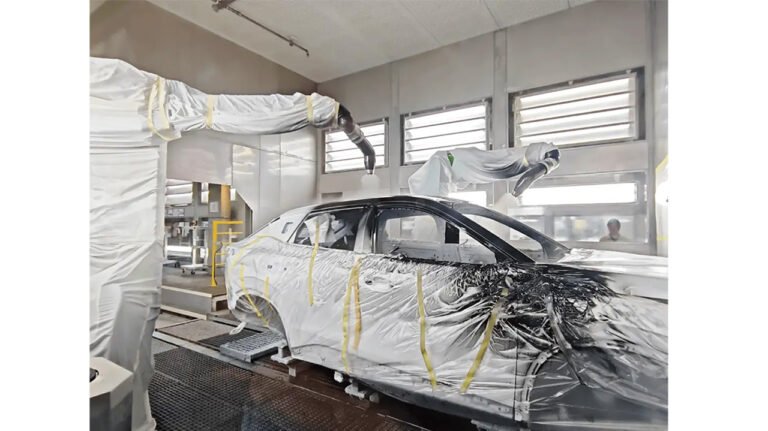
- Spraying: The conveyor line moves through the spray booth at a constant, preset speed. Spraying robots or automatic spray guns operate according to preset programs and synchronize tracking with the conveyor line speed to ensure even coating.
- For Complex Workpieces: Hangers may have rotation capabilities (via friction wheels or motors), allowing workpieces to rotate while moving for all-angle coverage.
- Leveling and Curing: After spraying, workpieces enter the leveling section (allowing the paint to flow evenly) and then proceed to the oven/drying tunnel (curing by hot air, infrared, or UV). The conveyor line must withstand high-temperature environments.
- Cooling and Unloading: Cured workpieces are cooled in a cooling section and then conveyed to the end for manual or robotic unloading.
- Empty Hanger Return: Empty hangers return to the loading area via the conveyor system (usually a lower track level), completing the cycle.
3. Key Technologies and Features
- Synchronization Technology: Spraying robots must synchronize their motion precisely with the moving workpiece, which is core to achieving high-quality automatic spraying.
- Accumulation Function (Optional): In more advanced systems, the conveyor line has an “accumulation” function. Workpieces can pause and accumulate at non-spraying stations (e.g., loading, unloading, maintenance) without stopping the entire line, improving flexibility.
- Adjustable Speed: Line speed can be adjusted according to process requirements (e.g., coating thickness, curing time).
- Flexibility: Through identification systems and programmable controls, mixed-model production can be achieved, meaning different workpieces can be painted on the same line with automatic parameter switching.
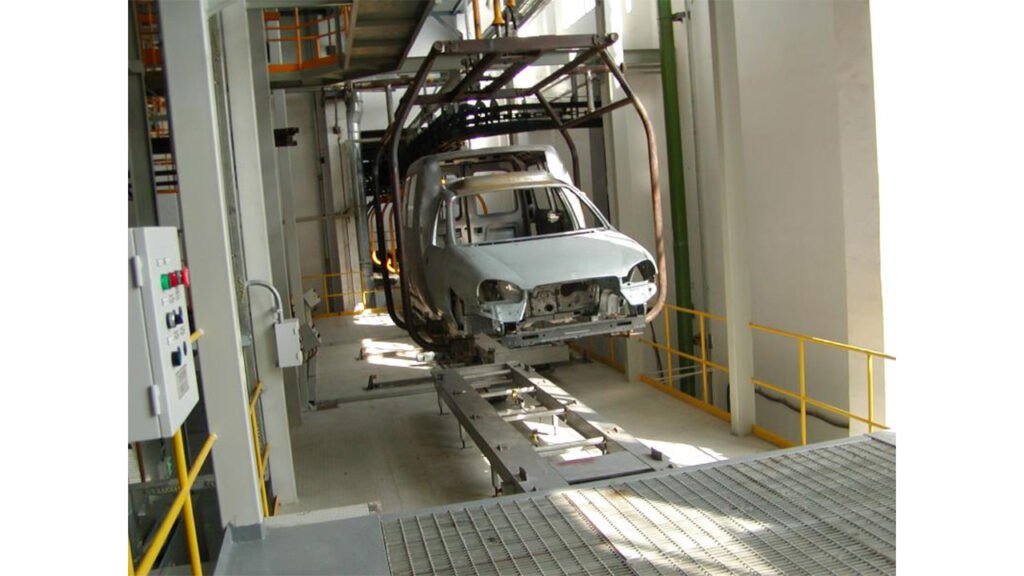
4. Main Application Areas
- Automotive Industry: Vehicle body and component painting.
- Home Appliance Industry: Spraying of refrigerator, air conditioner, washing machine casings.
- Metal Furniture and Building Materials: Doors, windows, filing cabinets, aluminum profiles.
- General Industry: Hardware tools, electronic device casings, toys, etc.

5. Selection and Design Considerations
- Workpiece Characteristics: Size, weight, shape, material.
- Process Requirements: Coating type (paint, powder), film thickness requirements, production cycle time (capacity).
- Workshop Conditions: Available space, ceiling height, ambient temperature/humidity.
- Automation Level: Manual spraying, automatic spraying, or human-robot collaboration.
- Maintenance and Cost: Initial investment, operating energy consumption, ease of maintenance.