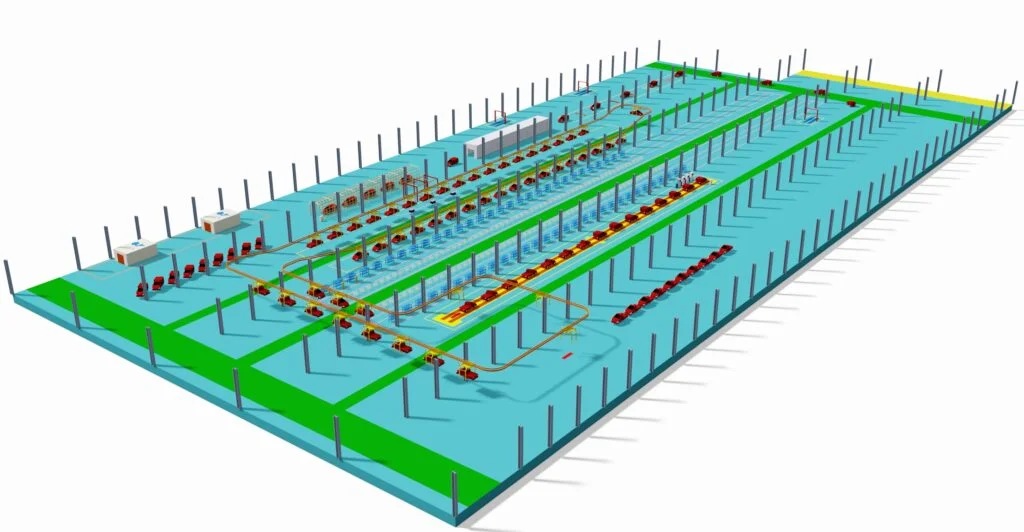
Automobile Assembly Lines are suitable to Produce 4 wheelers, Cars, Sedans, SUVs, Automobiles, EVs, Mini Vans, Hybrid Models and so on. (Sometimes, suitable for the production of pickups.)

Steps to Provide an Automotive Assembly Line for a Customer
Phase 1: In-Depth Requirements Analysis & Strategic Planning
This is the foundation of the project, determining the technical direction and investment scale of the entire line.
- Product Engineering Analysis:
- Platform & Models: Determine whether it’s for a single model or mixed-model production (flexibility). Understand the platform architecture, body materials (steel, aluminum, composites).
- Product Data: Obtain complete vehicle BOM, 3D models, 2D drawings, especially critical assembly dimensions for the chassis, powertrain, and interior/exterior trim.
- Lifecycle: Understand the vehicle model’s lifecycle and whether the production line needs to allow for future upgrades or new models.
- Manufacturing Strategy & Capacity Planning:
- Production Takt Time: This is the absolute core. Calculate the second-level takt time based on annual production volume and operating schedule.
- Operating Schedule: Determine the number of shifts, working days per year, and required equipment uptime.
- Process Planning: Collaboratively define the boundaries of the four main shops (Stamping, Body Shop, Paint Shop, General Assembly). The focus is typically on the Assembly area.
- Capacity & Lean Production:
- Line Balancing: Analyze the operation time at each station, optimize task allocation, eliminate bottlenecks, and bring each station’s time as close as possible to the takt time.
- Logistics Plan: Plan the material delivery mode from suppliers to the line-side (sequencing, kanban, call systems, AGV/AGC, etc.).
- Automation & Intelligence Level:
- Define which stations must be automated and which are suitable for manual work.
- Define requirements for Smart Manufacturing and Data Traceability: Is an MES system needed? Are critical torques 100% recorded and traceable? Is an ANDON system required?
- Site & Infrastructure:
- Conduct a detailed survey of the plant conditions: area, ceiling height, floor load-bearing capacity, and utilities (power capacity, compressed air, network).
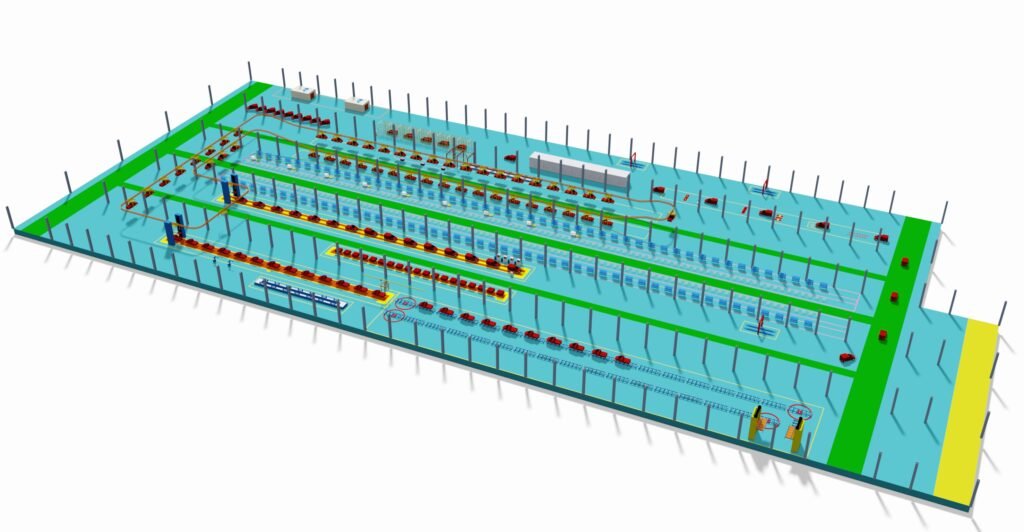
Phase 2: Detailed Solution Design & Engineering Development
(Select configurations based on your needs—some equipment are optional. Feel free to contact us for further details)
Transform the strategy into executable, detailed technical blueprints.
- Process Solution Design:
- Line Layout: Use CAD/3D software for detailed plant layout design, planning the material flow and spatial relationships between the main lines (Interior, Chassis, Final), sub-assembly lines (Doors, Cockpit, Engine Front Axle), and test lines (Wheel Alignment, Headlight Test, Roller Test).
- Process Sheets: Develop detailed work instructions for each station, including operation content, tools, materials, and quality requirements.
- Automation Solution Design:
- Mechanized Equipment: Design the conveying system, determining the drive and control systems.
- Robotic Applications: Plan robotic workstations, perform simulation to ensure reachability, cycle time, and safety.
- Special Purpose Equipment: Design non-standard automated equipment.
- Control System & IT Design:
- Electrical Control: Design the PLC network architecture, electrical schematics, and control panel layouts.
- Data Collection & Traceability: Design systems using RFID, barcodes, etc., for automatic vehicle identification and data collection at key stations, integrated with the MES.
- ANDON System: Design systems for material, quality, and equipment calls to enable transparent production management.
- HMI Design: Design user-friendly interfaces for operators and maintenance personnel.
- Logistics & Auxiliary Facility Design:
- Design line-side supermarkets, racks, and containers.
- Plan the placement and management of tools.
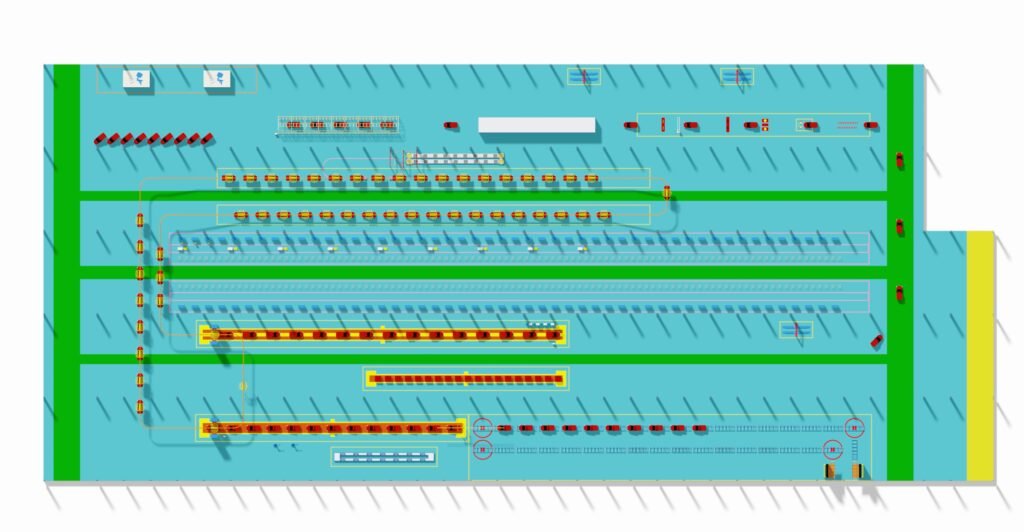
Phase 3: Procurement, Manufacturing
Transform the design blueprints into physical equipment.
- Supply Chain Management:
- High-quality components and custom fabricated parts.
- Strictly manage supplier delivery schedules and quality.
- Production:
- Perform machining, structural welding in-house or at partner facilities.
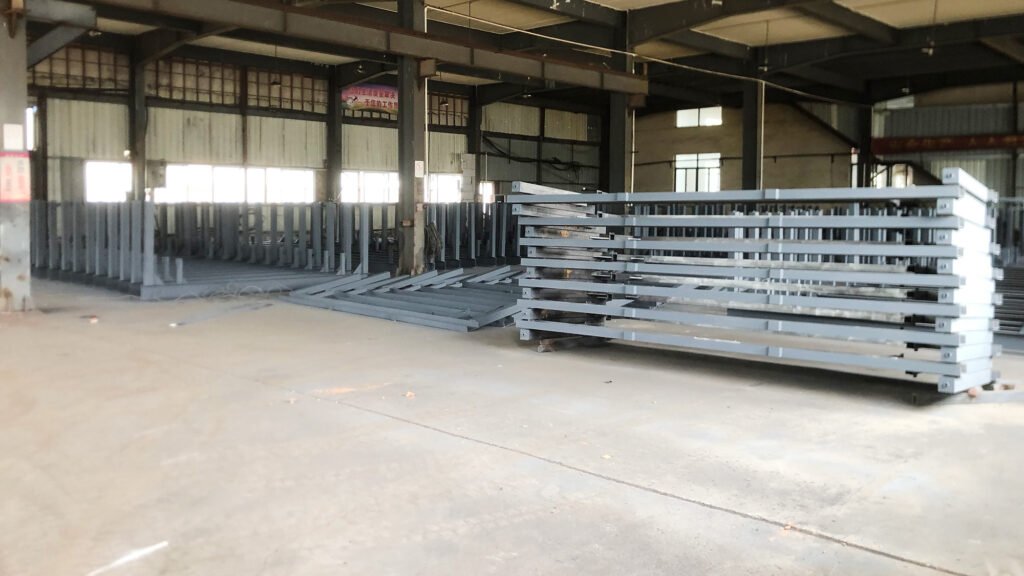
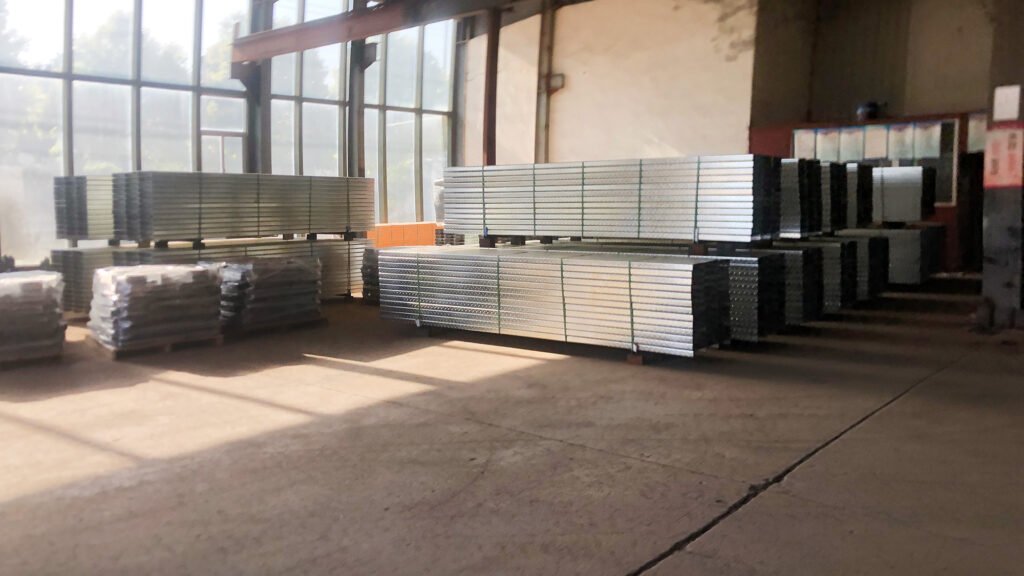






Phase 4: On-Site Installation, Commissioning
Assemble the “parts” into a “living” production line at the customer’s plant.
- Site Preparation & Equipment Move-In:
- Ensure the customer’s civil works and infrastructure are ready.
- Unpack, move, and position equipment.
- Mechanical/Electrical Installation:
- Install frames, conveyors, robots, platforms, etc.
- Complete all cable laying and pneumatic piping connections.
- On-Site Commissioning & Integration:
- Individual Equipment Commissioning: Power up and test basic functions of each device.
- Line Integration Commissioning: Integrate the entire conveying system for no-load operation.
- Commissioning with Vehicles/Carriers:
- Slow-Speed Debugging: Run with vehicle bodies or process carts at speeds lower than the takt time to verify all equipment works together.
- Takt Time Debugging: Gradually increase speed until the design takt time is reached, continuously optimizing.
- MES/Traceability System Integration Debugging: Verify the correctness and integrity of the vehicle data flow.
- Trial Run:
- SOP: Support the customer through low-volume trial production, producing the first saleable vehicles using real parts.
- Production Ramp-Up: Assist the customer in gradually increasing production speed from low rate to full capacity at the design takt time.
Phase 5: Training & Long-Term Support
Ensure the customer can operate the production line independently and efficiently.
- Comprehensive Training:
- Provide tiered training for operators, maintenance engineers, and production supervisors.
- Training content covers safe operation, daily checks, troubleshooting, and program backup.
- Documentation Handover:
- Deliver a project documentation, including: operation manuals, maintenance manuals, spare parts lists, etc.
- After-Sales & Continuous Support:
- Provide quick-response service during the warranty period.
- Supply spare parts and offer remote technical support.
Characteristics of an Automotive Assembly Line
Looking for VIN marking machines? Contact us for more information.
Need Filling Machines? Get expert support—request a quote or let’s talk about your project.
Looking for air compressors? Contact us for more information.
Need assembly tools or other auxiliary equipment? Contact us for more information.
