Automotive Refilling Equipment—Filling Equipment—Automobile Filling Machine
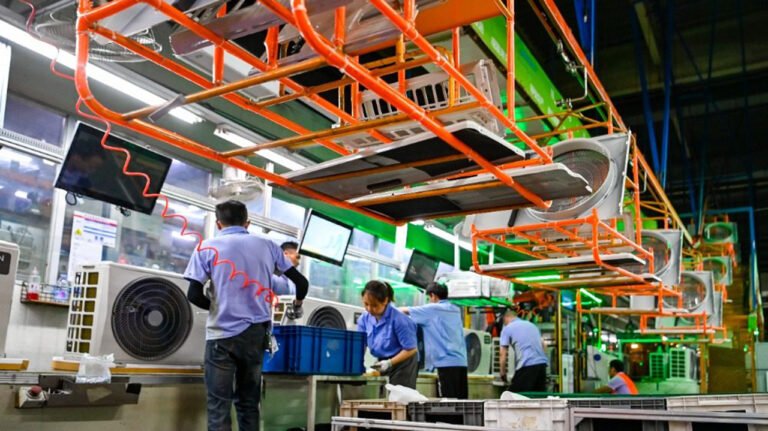
Automotive refilling/filling equipment is crucial in vehicle manufacturing, referring to the dedicated machinery used to fill liquids, gases, or lubricants into various automotive systems.
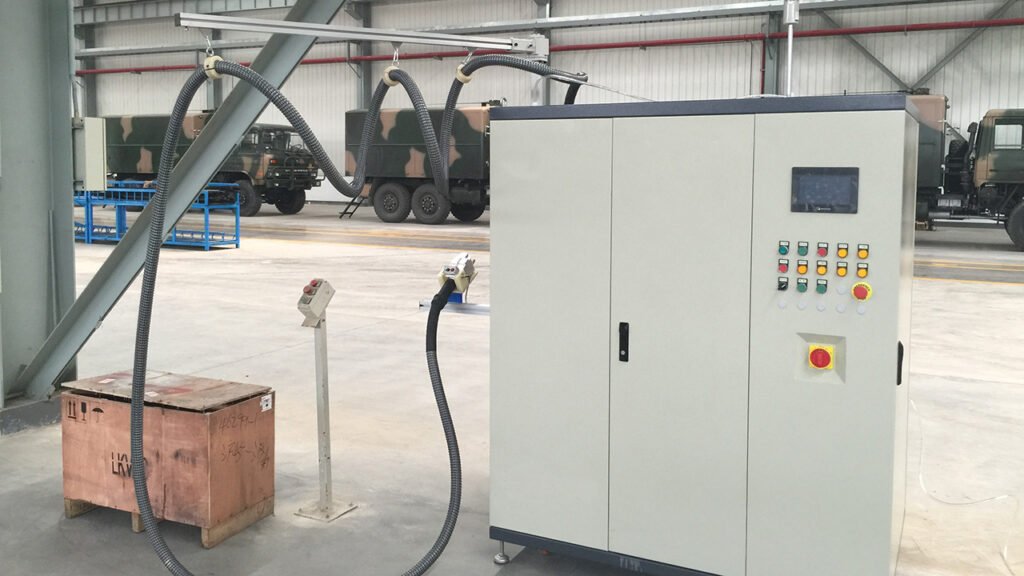

I. Refilling Equipment Used in Automotive Manufacturing Plants (OEMs)
On the final assembly line, refilling is a core process requiring high precision, high speed, full automation, and data traceability.
Key Media and Corresponding Equipment:
- Refrigerant Charging Station
- Purpose: To charge the vehicle’s air conditioning system with refrigerant (e.g., R-134a, R-1234yf) and compressor oil.
- Features: Fully automated vacuum evacuation, leak testing via pressure hold, and precise charging of refrigerant and oil based on vehicle model parameters. Data is directly uploaded to the Manufacturing Execution System (MES).
- Fuel Dispenser
- Purpose: To add a small amount of starter fuel to the new vehicle’s fuel tank.
- Features: Explosion-proof design, precise control of fill quantity.
- Coolant/Washer Fluid Filling Station
- Purpose: To fill engine coolant and windshield washer fluid.
- Features: Multiple nozzles for simultaneous, high-speed filling. Coolant stations often include vacuum or pressure equipment to remove air from the system.
- Brake Fluid Filling and Bleeding Equipment
- Purpose: To fill the brake hydraulic system with fluid and perform automated bleeding (crucial for removing air from ABS/ESP system modules).
- Features: Integrates filling, bleeding, and pressure testing functions. This is safety-critical process equipment.
- Powertrain/Battery Coolant Filling Station (For New Energy Vehicles – NEVs)
- Purpose: To fill specialized coolant into the battery pack and motor cooling systems of electric or hybrid vehicles.
- Features: Extremely high requirements for cleanliness, dryness (moisture control), and electrical insulation. Typically employs vacuum filling technology to ensure the system is free of air pockets.
- Transmission Fluid Filling Station
- Purpose: To fill automatic transmissions or reducers with specific fluid.
- Features: High-precision, quantitative filling. Some equipment includes heating functions to reduce fluid viscosity.
- Grease Lubrication Equipment
- Purpose: To apply a precise amount of grease to locations like door hinges and locks.
- Features: Often involves robots with dispensing guns for multi-point, quantitative application.
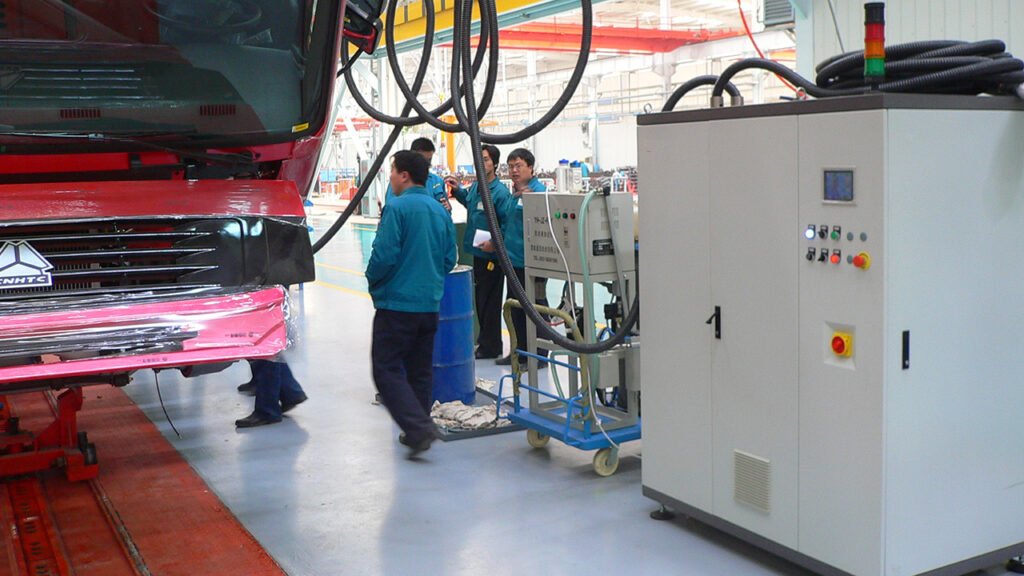

Core Technical Features of OEM Refilling Equipment:
- Vacuum Filling: The mainstream technology. The system is evacuated first, then filled under negative pressure to ensure it is air-free, especially for A/C and cooling systems.
- Servo Drive/Mass Flow Meters: Enable ultra-high precision at the gram/milliliter level.
- Automatic Identification & Error-Proofing: Uses RFID or PLC to automatically identify the vehicle model and call up the corresponding filling program, preventing errors.
- Data Connectivity: All filling parameters (volume, time, results) are uploaded to the MES, enabling full lifecycle traceability.

II. Key Technologies and Development Trends
- Technological Core:
- Vacuum Technology: Ensures systems are air-free.
- Precision Metering Technology: Guarantees accurate fill volumes.
- Media Compatibility & Sealing Technology: Prevents cross-contamination between different fluids and equipment leaks.
- Safety & Explosion-Proof Technology: Especially for handling fuels, refrigerants, etc.
- Development Trends:
- Smart & IoT Integration: Remote equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, cloud-based recipe management.
- Adaptation for New Energy Vehicles: Surging demand for specialized equipment for battery coolant, e-motor oils, and high-voltage systems as EVs proliferate.
- Environmental Focus: Stricter standards for refrigerant recovery/recycling to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Integration & Modularity: Combining multiple refilling functions into a single unit or using modular designs to suit different workshop needs.