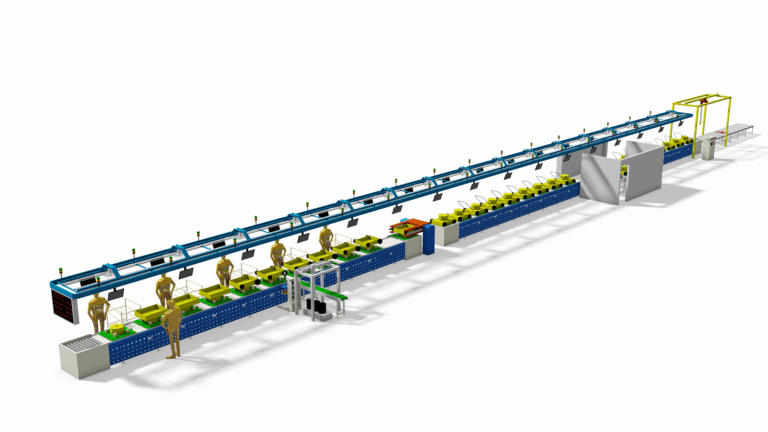
How to set up a Tricycle Assembly Line factory? Tricycle Assembly Line Design and Fabrication
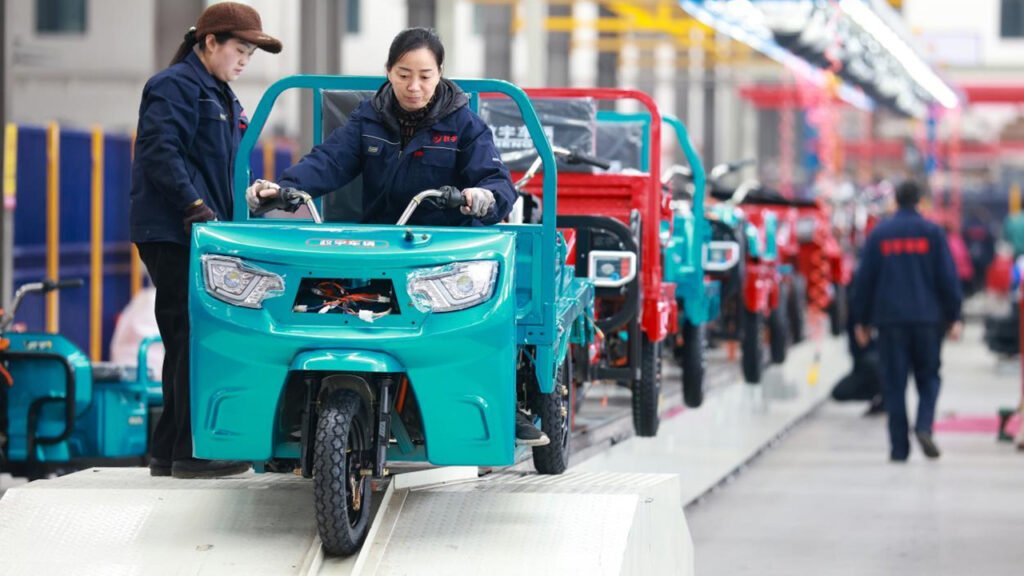

Establishing a tricycle assembly factory is a systematic investment project that requires comprehensive consideration of multiple aspects such as market, capital, technology, and management. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide to help you plan and implement this project.
Phase I: Strategic Decision-Making and In-Depth Feasibility Study
Before committing any funds, several core questions must be answered:
- In-Depth Research on the Target Country (This is the most critical step)
- Policies and Regulations:
- Investment Policies: Restrictions on foreign shareholding, land ownership, profit repatriation rules.
- Industrial Policies: Access standards for the automotive/motorcycle industry, local content requirements, tax incentives (e.g., tax holidays).
- Product Regulations: Vehicle certification systems, safety, environmental (emissions/noise) standards, battery safety certifications (if applicable).
- Market Analysis:
- Main competitors (local brands, international brands).
- Consumer preferences (load capacity needs, fuel/electric preference, road conditions, aesthetics).
- Sales channel structure (dealer networks, e-commerce penetration).
- Supply Chain Foundation:
- Availability of local suppliers for steel, plastics, simple stamping parts, etc.
- Local labor skill levels and wages.
- Status of infrastructure like ports, inland transportation, and electricity.
- Policies and Regulations:
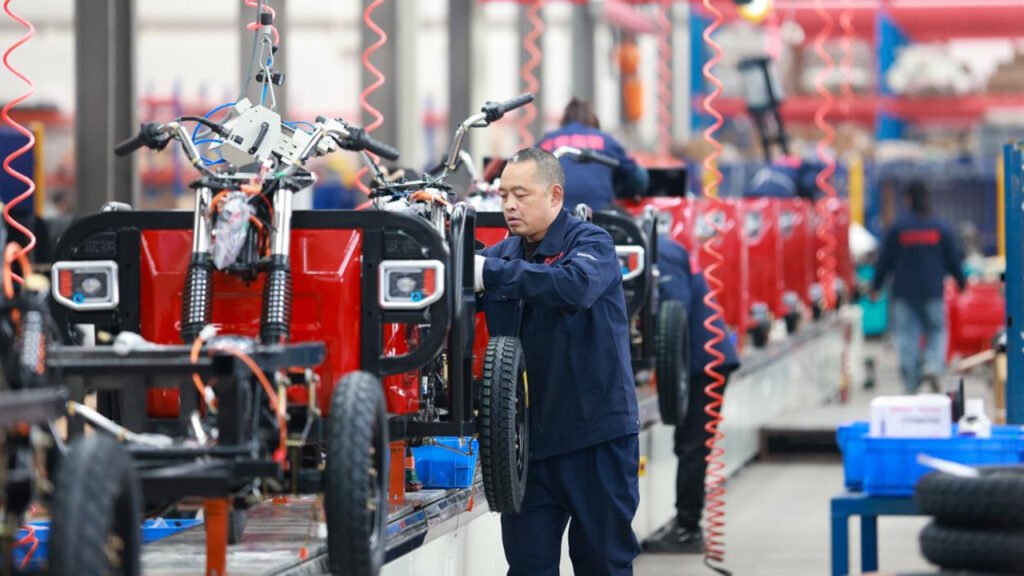

Phase II: Detailed Implementation Steps
- Legal Entity Establishment and Licensing
- Register a company in the target country.
- Obtain a “Manufacturing License” and “Investment Approval”.
- Apply for permits related to land use, environmental protection, fire safety, etc., for factory construction.
- Factory Planning and Construction
- Site Selection: Proximity to ports (for easy import of kits) or target markets, considering industrial park amenities and labor supply.
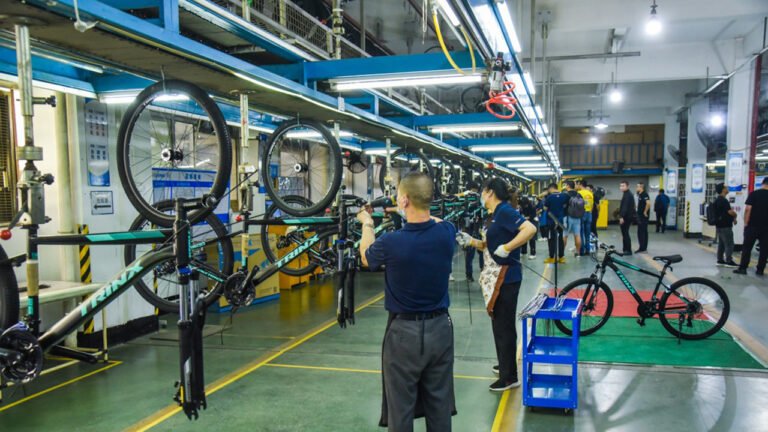
- Factory Layout Design: Design based on process flow (Receiving Area – Storage – Welding Line – Painting Line – Assembly Line – Testing Line – Finished Goods Area). Leasing a standard factory building is feasible initially.
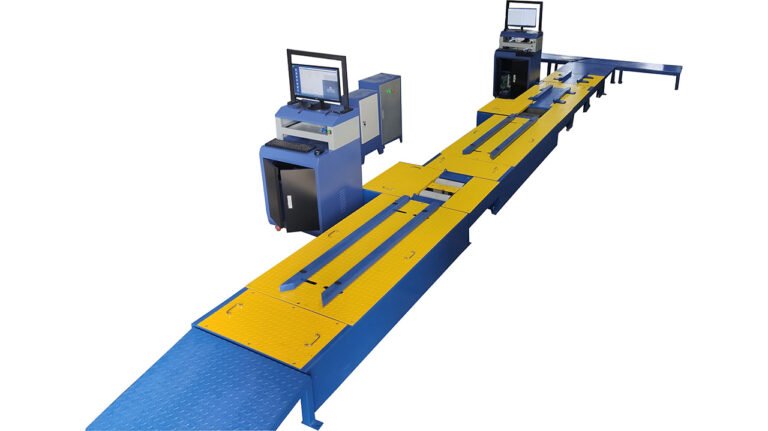
- Equipment Procurement: Source some from China (good cost-performance), others locally or from other countries. Essential equipment includes:
- Welding equipment (welders, jigs, fixtures)
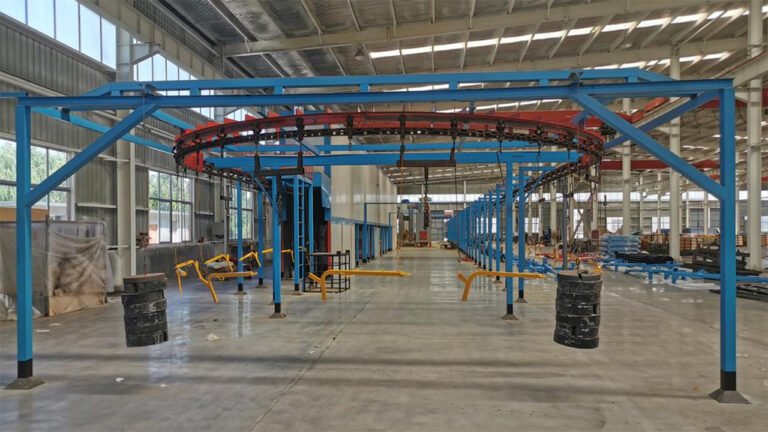
- Painting equipment (spray booths, baking ovens) or outsource painting
- Assembly line (conveyors, lifts, tools)
- Testing equipment (torque wrenches, light testers, brake testers, road test area)
- Supply Chain Setup (Core Challenge)
- Establish Strategic Partnerships with Chinese Core Suppliers: Identify 1-2 reliable suppliers for frames, engines/motors/controllers, rear axles, and sign long-term supply agreements. Ensure consistency in drawings and quality standards.
- Develop Local Secondary Suppliers: Gradually localize the procurement of tires, batteries (may be sourced locally), seats, wiring harnesses, lights, standard parts, etc., to reduce costs and meet local content requirements.
- Logistics and Customs Clearance: Find an experienced international freight forwarder to handle the shipment of knocked-down kits in containers and customs clearance at the destination port.
- Team Building and Training
- Core Expatriate Team: Hire experienced Production Managers, Process Engineers, Quality Managers from China for initial setup and training (3-12 months).
- Local Team Recruitment: Recruit local production line supervisors, workers, procurement, administration, and sales staff.
- Systematic Training: Conduct hands-on training in welding, assembly, and quality inspection at the Chinese partner’s factory or the local factory. Establish Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
- Product Certification and Mass Production
- Prototype Assembly: Assemble several prototype vehicles using the first batch of tricycle kits.
- Trial Production and Mass Production: Start with small-batch production to optimize processes, then gradually ramp up to designed capacity.
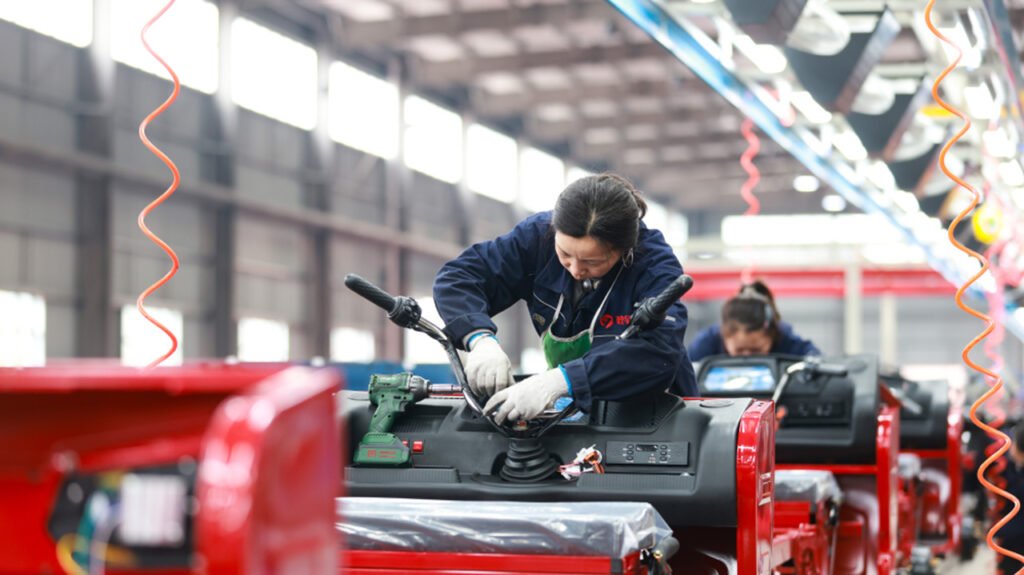

Phase III: Key Success Factors
Keys to Success:
- Find a Strong and Reliable Chinese Partner: This solves most challenges related to technology, core quality, and supply chain.
- Deeply Understand and Comply with Local Regulations: Laws and certifications are non-negotiable red lines.
- Localized Operations Management: Respect local culture and gradually localize the management team.
- Focus on Quality Control: Establish quality standards consistent with the Chinese headquarters to protect brand reputation.
Actionable Advice for Foreign Clients
- Form a Professional Project Team: The team must include members knowledgeable about the target country’s laws, manufacturing, and the Chinese supply chain.
- Conduct a Detailed Feasibility Study: Hire a local consulting firm to complete a comprehensive report.
- Visit China for On-Site Inspections: Tour potential partners’ factories and negotiate cooperation intentions.
- Invest in Phases: Start with the SKD mode to validate the process and market with minimal investment, then gradually transition to CKD.
In summary, the optimal path for a foreign client to establish a tricycle assembly factory is: Select a reliable Chinese technical partner(assembly line supplier and tricycle components supplier), start with SKD assembly, and based on a deep understanding of local market regulations, progressively achieve supply chain and management team localization. This is a systematic project requiring patience, expertise, and sufficient capital.