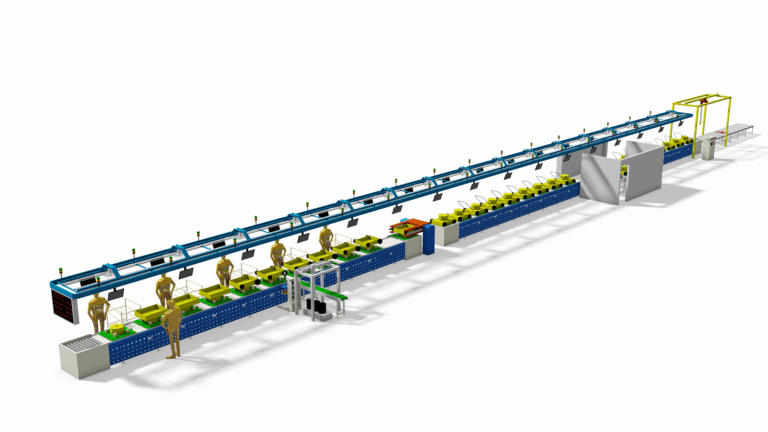
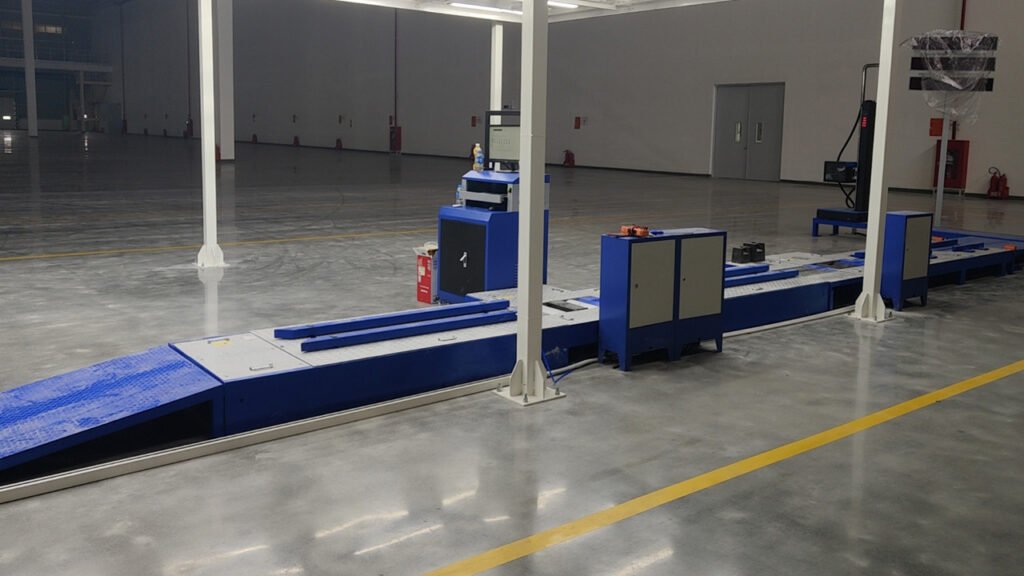
Motorcycle Testing Line—Motorcycle Performance Test Equipment
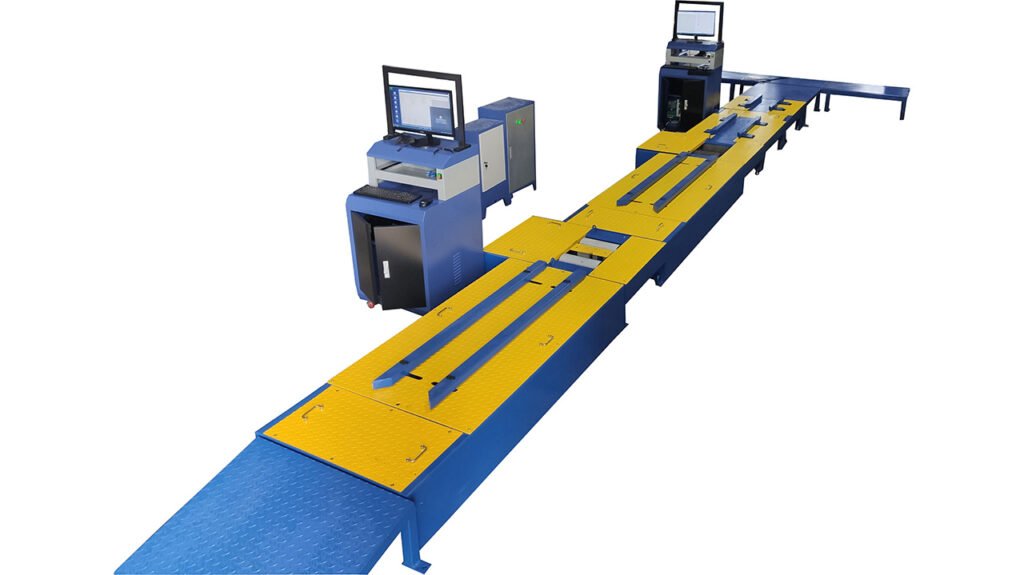

Motorcycle Testing Lines are suitable to Test 2 wheel Motorcycles, 2 wheel Scooters, 2 wheel Electric-cycles, 2 wheel E-Bikes. (For some models, we also can supply you the testing lines for both of 2 wheelers and 3 wheelers/tricycles.)

Introduction to Motorcycle Testing Equipment
This is an overview of motorcycle testing equipment. Such equipment is primarily used for final factory inspection, maintenance, diagnostics, and vehicle annual inspections (safety/emissions) to ensure vehicle safety, performance compliance, and environmental standards.
The equipment is categorized below by its primary function:
1. Safety Performance Testing Equipment
- Motorcycle Brake Tester
- Function: Precisely measures the maximum braking force, brake force balance, and drag force of the front and rear wheels.
- Principle: Rollers drive the wheels to rotate. When brakes are applied, the device measures the resistance on the rollers to calculate braking force.
- Importance: Directly relates to braking safety; a mandatory item for annual inspections.
- Motorcycle Wheel Load Scale
- Function: Measures the load (weight) on the front and rear wheels.
- Importance: Provides critical data for calculating the braking ratio (braking force as a percentage of wheel load), which is fundamental for brake testing.
- Motorcycle Headlamp Tester
- Function: Measures the luminous intensity (brightness, in candela – cd) of the high beam and the alignment/cut-off line position of the low beam.
- Principle: Optical measurement. The vehicle is stationary, and the tester aligns with and measures the headlamp.
- Importance: Ensures safe nighttime illumination without blinding others.
- Motorcycle Side Slip Tester
- Function: Detects the lateral slip of the front wheel during straight-line motion.
- Principle: Measures lateral force generated by the wheel as it passes over a laterally movable sliding plate.
- Importance: Indirectly reflects the accuracy of front wheel alignment (e.g., caster angle, camber angle), affecting straight-line stability.
- Motorcycle Speedometer Tester
- Function: Calibrates the speedometer indication error (actual speed vs. displayed speed).
- Principle: Rollers drive the rear wheel to simulate road conditions, calculating true speed by measuring roller RPM.
- Standard: Typically requires displayed speed ≥ actual speed, within a permitted error range (e.g., 0-10%).
- Motorcycle Shock Absorber Test Bench (Equipped in some advanced inspection lines)(optional)
- Function: Measures the damping force and recovery performance of shock absorbers by oscillating the wheel.
- Importance: Determines if shock absorbers are leaking or failing, which affects handling and comfort.
2. Emission & Powertrain Testing Equipment
- Motorcycle Exhaust Gas Analyzer
- Function: Measures concentrations of pollutants in engine exhaust such as CO (Carbon Monoxide), HC (Hydrocarbons), NOx (Nitrogen Oxides).
- Types:
- 4-Gas / 5-Gas Analyzer: For spark-ignition engines (gasoline), measures CO, HC, CO₂, O₂, (NOx).
- Opacity Meter/Smoke Meter: For compression-ignition engines (diesel motorcycles, less common), measures exhaust smoke density.
- Motorcycle Chassis Dynamometer (optional)
- Function: Simulates road load resistance for power testing, emission durability testing, fuel consumption testing.
- Principle: The vehicle’s rear wheel is placed on rollers. A load-absorbing unit (eddy current, electric, etc.) applies resistance to simulate various driving conditions.
- Engine Diagnostic Analyzer / Motorcycle-Specific Diagnostic Tool (optional)
- Function:
- Reads and clears fault codes (OBD) from the electronic fuel injection system.
- Views engine data streams (RPM, coolant temperature, throttle position, injection pulse width, oxygen sensor signal, etc.).
- Performs actuator tests (e.g., injectors, ignition coils, idle air control valve).
- Function:
- Ignition Timing Light / Fuel Injector Tester (optional)
- Function: Checks if ignition timing is accurate; tests injector flow rate, spray pattern, and sealing.

3. Component & Characteristic Testing Equipment (optional)
- Axle Weight/Sprung Mass Test Platform: Used in R&D to measure weight distribution and center of gravity.
- Vibration and Noise (NVH) Testing System: Used to evaluate overall vehicle Noise, Vibration, and Harshness performance.
- Frame/Component Strength Tester: Conducts fatigue and strength tests on critical parts like frames, shocks, and handlebars.
- Water Spray Test Equipment: Tests sealing and waterproof performance of the whole vehicle or components.
- Light detection channel: Mainly observe whether there is any damage on the vehicle’s surface.
4. Trends: Intelligence & Integration
Modern motorcycle inspection lines are moving towards high automation and intelligence:
- Integrated Control System: Automatically collects, processes, and summarizes data from brake, side slip, speed, and headlamp stations to generate a unified test report.
- Automatic Vehicle Identification(optional): Uses RFID or cameras to identify vehicle information, automatically linking it to test data.